This 27-year-old patient presented with postprandial epigastric/stomach pain and a high level of dysphagia. Her OGD was normal with MBI = 14 and Lupus A. Stationary high- resolution manometry with impedance was carried out.
High-Resolution Manometry




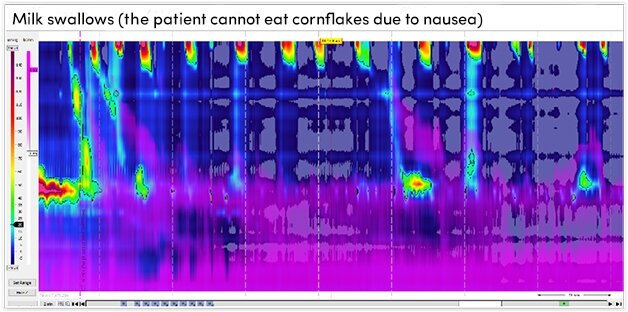


HRM results were as follows:
- The upper oesophageal sphincter was hypotensive and showed complete relaxation on wet swallows.
- The oesophagus produced normal peristalsis and 200 ml milk swallows (the patient could not have cornflakes due to nausea) did not show characteristic abdominal contraction and no vomiting.
- The patient perceived high dysphagia and stomach pain which was not explained by HRM motility.
- The lower oesophageal sphincter was normotensive and showed complete relaxation on wet-swallows.
- There was no evidence of hiatus hernia.
These results based on the Chicago Classification showed that the patient exhibited normal oesophageal motility.
Interpretation
There was no evidence for rumination syndrome. During solid swallows, the patient perceived high dysphagia which seemed to be correlated with some retention (detected by impedance sensors) above the transition zone due to poor motility in the upper third of the oesophagus. When there was normal proximal motility there was no retention and no symptoms.
Next Steps
It is suggested that barium swallows with solid boluses may provide further information.










